
NET platform might not face this issue at all. have been the initiatives from M$ to solve this problem. However, at times system upgrades often breaks other programs when there is a version mismatch between the shared DLL files and the program that requires them. This too causes applications to ship with a lot of DLL files. Good applications also try to not load the DLL files until they are absolutely required, which reduces the memory requirements. Installed applications also use DLL filesĭLL files also becomes a form of separating functionalities physically as explained above. Each functionality is kept separately in different DLL files so that only the required DLL files will be loaded and thus reduce the memory constraints on the system.
#Dll files com code#
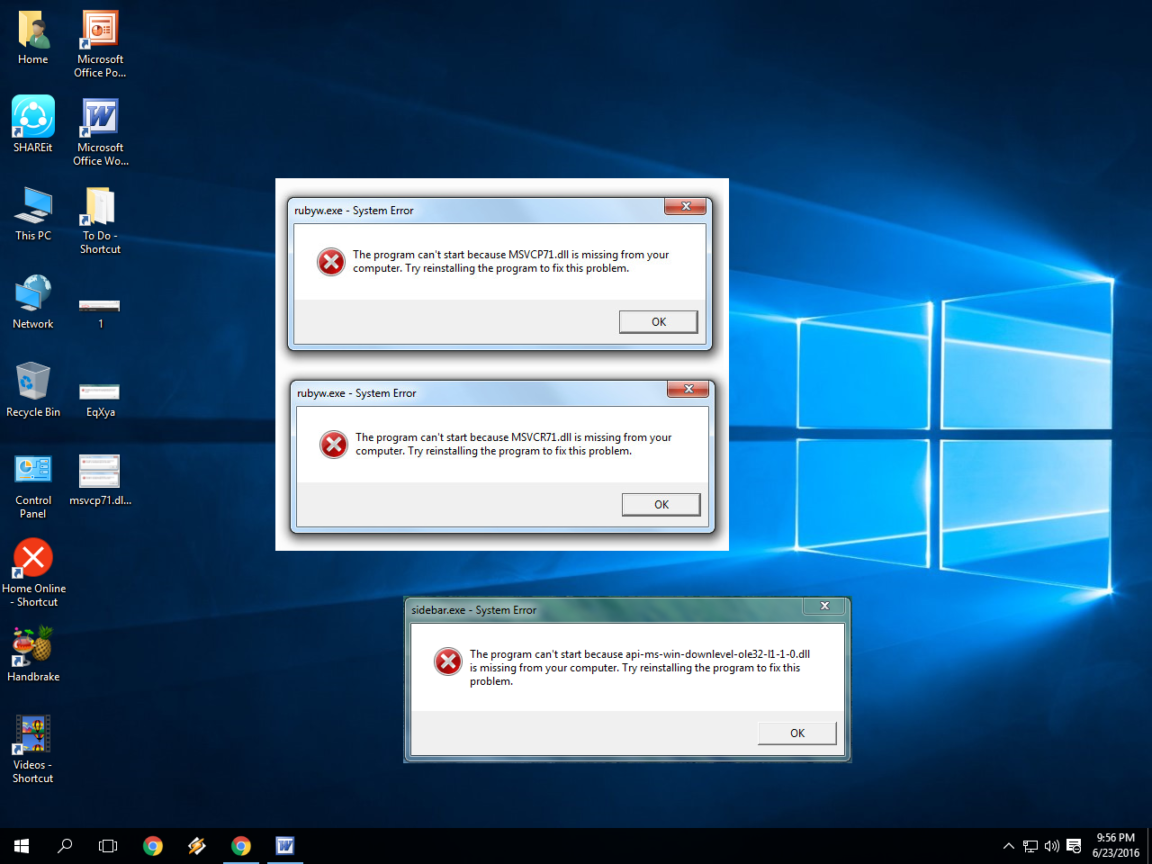
Most of the system functionality is exposed to a user program in the form of DLL files as they are a standard form of sharing code / resources. There are so many of them in the system folders This is debugged easily using any dependency walker tools, like Dependency Walker. If one of these DLL files in the chain of dependency is not found, the application will not load. In the same way that an application requires a DLL file, a DLL file might be dependent on other DLL files itself.

If any of these are not found the system will not be able to start the process at all. Most applications will load the DLL files they require at startup. Unlike applications, these cannot be directly executed, but an application will load them as and when they are required (or all at once during startup). Also the sources of this answer.ĭLL files are binary files that can contain executable code and resources like images, etc. Please check MSDN or Wikipedia for further reading. A program uses the GetProcAddress to load a function or LoadResource to load a resource. A static library cannot be changed once it is compiled within the EXE.Ī DLL can be updated individually without updating the EXE itself.Ī program loads a DLL at startup, via the Win32 API LoadLibrary, or when it is a dependency of another DLL.
A dynamic library is a stand-alone file.Ī DLL can be changed at any time and is only loaded at runtime when an EXE explicitly loads the DLL.
#Dll files com .exe#
You don't normally see static libraries though on your computer, because a static library is embedded directly inside of a module (EXE or DLL). The main difference is that static libraries are linked to the executable at compile time whereas dynamic linked libraries are not linked until run-time.
#Dll files com windows#
In windows the file extensions are as follows: Static libraries (.lib) and dynamic libraries (.dll). On virtually all operating systems, there are 2 types of libraries. NET libraries.Ī DLL contains functions, classes, variables, UIs and resources (such as icons, images, files. DLLs can also contain COM components and.
#Dll files com portable#
Both EXE and DLLs are based on the Portable Executable (PE) file format. That is to say, DLLs are MS's implementation of shared libraries.ĭLLs are so much like an EXE that the file format itself is the same. Dynamic Link Libraries (DLL)s are like EXEs but they are not directly executable.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
